Fencing (STONITH) is an important mechanism in cluster to avoid the data corruption on shared storage. It also helps to bring the cluster into the known state when there is a split brain occurs between the nodes. Cluster nodes talks to each other over communication channels, which are typically standard network connections, such as Ethernet. Each […]
Redhat-LINUX
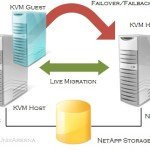
RHEL 7 – Pacemaker – Configuring HA KVM guest – Part 7
If you have followed the KVM article series in UnixArena , you might have read the article which talks about the KVM guest live migration. KVM supports the Guest Live migration (similar to VMware vMotion) but to provide high availability , you need need a cluster setup . (Like VMware HA). In this article ,we […]
RHEL 7 – Pacemaker – Cluster Resources/Group Management – Part 6
In Pacemaker/Corosync cluster (RHEL 7 HA), resources management and resource group management are important tasks . Depends on the cluster HA services, you might need to configure N-number of resources. In most of the cases , you might need to start set of resources sequentially, and stop in the reverse order. To simplify this configuration, Pacemaker supports […]
RHEL 7 – Pacemaker – Cluster Resource Agents Overview – Part 5
Resource agents plays an important role in cluster management. Resource agents are multi-threaded processes that provides the logic to manage the resources. Pacemaker has one agent per resource type. Resource type could be a File-system , IP address , databases, virtual-domain and more. Resource agent is responsible to monitor, start , stop,validate , migrate , promote and demote […]
RHEL 7 – Configuring Pacemaker/Corosync – Redhat Cluster – Part 4
In this article, we will see that how to configure two node Redhat cluster using pacemaker & corosync on REHL 7.2. Once you have installed the necessary packages, you need to enable the cluster services at the system start-up. You must start the necessary cluster services before kicking off the cluster configuration. “hacluster” user will be […]
RHEL 7 – Installing Redhat Cluster Software (Corosync/pacemaker) – Part 3
In this article, we will see that how to install Redhat cluster software (Pacemaker) on RHEL 7. If you have valid redhat subscription , you can directly configure redhat repository and install the packages. It also available in the RHEL 7 ISO image as an Add-on Package. Unlike previous redhat cluster releases , Redhat cluster 7 installation […]
Perform Live Migration on Linux KVM – Part 11
In KVM , you can migrate the running virtual machines from one KVM host to another without any downtime. Live migration works well if both the KVM hosts have access to the same storage pool. To make the storage pool accessible on both the KVM hosts, you need to use NFS or GFS2 filesystem(cluster filesystem). […]
Linux KVM – Change libvirt VM image store path – Part 10
In KVM , VM images are stored in /var/lib/libvirt/images directory by default. There might be the space limitation since /var filesystem lives under root-vg. In KVM virtualization, everyone would prefer to store VM images in central repository to migrate running VM from one hypervisor to another. In that case, you need to change the default path for the libvirt images […]
Linux KVM – How to add /Remove vCPU to Guest on fly ? Part 9
Does KVM support vCPU hot-plug ? Will Linux KVM guest can recognize the newly added vCPU’s ? The answer is “YES” off-course. Like KVM memory management, you can add/remove vCPU’s to active VM using “virsh” command. But this works if you have configured the KVM guest with Maximum vCPUs parameter. So while deploying the new […]
Linux KVM – How to add /Remove Memory to Guest on Fly ? Part 8
If the application/DB is demanding more Memory, you need to adjust the VM’s memory limit accordingly. KVM supports dynamic memory addition when you have configured the VM’s with Maximum memory limits. There are two parts to the VM configuration. 1. Maximum Limits 2. current allocation. At any point in time, you can’t exceed the maximum […]